Siding Cost Per Square Foot A Comprehensive Guide
Siding cost per square foot is a crucial factor in any home improvement project. Understanding the various materials, influencing factors, and regional variations is essential for informed decision-making. Different siding types, like vinyl, wood, and fiber cement, come with varying price points, and local market conditions play a significant role in overall costs. This guide will delve into the specifics, examining factors like material quality, installation methods, and regional price differences.
The following sections will detail the breakdown of costs for different siding materials, analyzing installation labor costs, and offering strategies for estimating and potentially saving money. Whether you’re a homeowner considering a DIY project or planning a professional installation, this comprehensive resource provides the necessary information to make an informed choice.
Introduction to Siding Costs
Siding is a crucial component of any home’s exterior, impacting its aesthetic appeal and overall value. Understanding the cost of different siding materials is essential for homeowners planning renovations or new construction. Accurate cost estimations depend on a variety of factors, and a comprehensive understanding of these elements allows for realistic budgeting.
Siding costs vary significantly depending on the material chosen. This is influenced by factors like material availability, labor rates, and the complexity of the installation. Local market conditions also play a significant role in determining the final price. A thorough understanding of these factors is vital to ensure a well-informed decision-making process.
Siding Materials and Cost Ranges
Various materials are available for siding, each with its own characteristics and price point. The cost of materials is a primary factor in determining the total project expense.
- Vinyl siding is a popular choice due to its affordability and low maintenance. Expect costs to range from $3 to $8 per square foot, depending on the style and quality of the vinyl.
- Wood siding offers a classic aesthetic but requires more upkeep. Its cost generally falls between $5 and $15 per square foot, with higher-end options potentially exceeding this range.
- Fiber cement siding combines the durability of cement with the aesthetic appeal of wood or vinyl. Installation costs typically range from $8 to $15 per square foot, often exceeding vinyl but being more cost-effective than wood.
Factors Influencing Siding Costs
Several factors significantly impact the overall cost of siding projects. Understanding these factors is key to accurate budgeting.
- Material cost is a significant contributor to the overall cost. The price of raw materials directly influences the final price of the project.
- Labor costs vary greatly depending on location and the complexity of the installation. Labor costs can be a substantial portion of the total project cost, especially for intricate designs or large projects.
- Installation complexity factors like the size of the house, the condition of the existing siding, and the presence of architectural details will affect the labor time and overall cost.
- Local market conditions, including material availability, labor rates, and demand, play a crucial role in determining the final price.
Average Cost Per Square Foot Comparison
The following table provides a general comparison of average costs per square foot for various siding materials. Keep in mind these are averages, and actual costs may vary based on the specific factors mentioned above.
| Siding Material | Average Cost per Square Foot |
|---|---|
| Vinyl | $5.00 – $7.00 |
| Wood | $7.50 – $12.00 |
| Fiber Cement | $8.00 – $14.00 |
Factors Affecting Siding Cost per Square Foot

Source: woodbridgehomesolutions.com
Numerous factors influence the cost of siding installation, making it crucial to understand these elements before embarking on a project. Understanding these variables empowers homeowners to make informed decisions, ensuring a budget-friendly and successful siding replacement.
Various aspects contribute to the final cost, from the type of siding material to the complexity of installation and the geographical location. The material quality, labor costs, and installation method all play significant roles in shaping the overall expense.
Material Quality and Brand Reputation
Different siding materials vary considerably in cost. Premium materials, often associated with higher brand recognition and superior durability, command a higher price point. For instance, composite siding, while offering a longer lifespan and low-maintenance features, typically costs more than vinyl siding. Likewise, cedar siding, known for its natural beauty, tends to be pricier than cheaper options like aluminum. This difference in cost directly reflects the material’s inherent properties, manufacturing processes, and perceived value.
Labor Costs
Labor costs are a substantial component of any siding project. Professional installation often requires specialized skills and equipment, leading to higher labor expenses. Factors like the complexity of the installation, the size of the house, and the availability of skilled labor in a particular region significantly influence the labor cost. DIY installations, while potentially more cost-effective, require considerable time and expertise to ensure a quality job. Inaccurate or poorly executed installation can lead to costly repairs in the long run.
Installation Methods
The choice between DIY and professional installation significantly impacts the overall project cost. While DIY projects can potentially save money on labor, the risk of errors or subpar results is high. Conversely, professional installation guarantees a higher level of quality, adherence to building codes, and potentially better warranties, though this comes with a higher cost. This decision depends on individual skills, available time, and the desire for a professional outcome.
Geographic Location
Geographic location plays a key role in material and labor costs. Material costs are influenced by factors like transportation, local availability, and demand. Labor rates also vary across different regions. For example, a coastal area might have higher material costs due to transportation factors, while a rural area may experience higher labor rates due to lower availability of skilled labor. The cost of living and local regulations also affect these variables.
Influence of Labor Costs on Total Cost per Square Foot
| Siding Type | Estimated Labor Cost per Square Foot (USD) | Total Cost per Square Foot (USD) – Example (including material) |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $5 – $10 | $15 – $25 |
| Composite | $7 – $12 | $20 – $30 |
| Cedar | $8 – $15 | $25 – $35 |
| Aluminum | $4 – $8 | $12 – $20 |
The table above provides a simplified illustration of the influence of labor costs on the total cost per square foot for various siding types. Remember that these are estimated values and actual costs may vary based on specific project details, local market conditions, and material choices. Factors like the size of the project, the complexity of the house’s design, and the level of craftsmanship required by the installer all play a role in determining the final cost.
Regional Variations in Siding Costs: Siding Cost Per Square Foot
Siding costs aren’t uniform across the country. Factors like labor rates, material availability, and local regulations significantly impact the final price. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for homeowners planning siding projects.
Regional differences in siding costs stem from variations in labor rates, material availability, and building codes. For example, areas with high demand for siding work might see higher labor costs, while regions with readily available materials may experience lower material expenses.
Cost Variations Across US Regions
Different parts of the US experience varying costs for siding installation. These variations are often linked to the cost of labor and materials, as well as local building codes and regulations. For example, areas with higher demand for siding work might see inflated labor costs. Conversely, regions with abundant material sources could result in lower material expenses.
Influence of Local Building Codes and Regulations
Local building codes and regulations play a pivotal role in shaping siding costs. These codes often dictate the types of materials permissible, installation standards, and required inspections. Areas with stricter codes might necessitate more specialized materials or more extensive inspections, leading to increased expenses. Furthermore, compliance with these regulations is paramount to avoid potential penalties or delays.
Examples of High-Cost and Low-Cost Areas
High-cost areas for siding installations often coincide with metropolitan areas and regions with high labor costs. Areas with abundant, readily available materials or lower labor costs tend to have lower siding installation costs. Examples include the coastal regions of California and the Northeast, where high labor rates and stricter building codes often push up costs. In contrast, areas in the Midwest or Southern regions, with potentially lower labor rates and abundant materials, often see lower installation costs.
Average Siding Costs per Square Foot by State (Estimates)
| State | Average Siding Cost per Square Foot (USD) |
|---|---|
| California | $10-15 |
| Texas | $7-12 |
| Florida | $8-13 |
| New York | $12-18 |
| Illinois | $8-14 |
| North Carolina | $7-12 |
| Washington | $11-16 |
| Pennsylvania | $9-15 |
| Georgia | $7-12 |
| Oregon | $10-15 |
Note: These are estimated averages and can vary based on the specific siding material, style, and complexity of the installation.
Siding Material Cost Breakdown
The cost of siding isn’t solely determined by the material itself; various factors contribute to the final price. Understanding these components helps homeowners make informed decisions. Different siding types have varying raw material costs, manufacturing processes, and associated labor expenses.
The price per square foot for siding is a complex calculation, influenced by numerous variables. Factors such as material thickness, quality, and regional variations in labor costs are crucial elements in the final cost breakdown. Understanding these nuances can assist in budgeting and choosing the most suitable siding option for a project.
Raw Material Costs
Different siding materials have varying raw material costs. Vinyl siding, for instance, relies heavily on polymers and additives, which can fluctuate in price based on market conditions and availability. Wood siding, while often perceived as a more natural option, is influenced by lumber prices, which are susceptible to seasonal changes and global supply chains. Steel siding’s cost is affected by fluctuating metal prices, while fiber cement siding relies on cement, sand, and fiber components, each with its own price volatility.
Manufacturing Processes and Technologies
Manufacturing processes and technologies play a significant role in shaping siding costs. Modern vinyl siding production often utilizes advanced extrusion techniques, potentially affecting the quality and durability of the product, which can be reflected in the final price. Similarly, advancements in steel production, such as galvanizing processes, may improve the lifespan of steel siding but may also increase its initial cost. The manufacturing processes for fiber cement siding also contribute to the price; the complex process of mixing and shaping the material influences the final cost.
Material Thickness and Quality
The thickness and quality of siding materials directly impact their cost. Thicker vinyl siding may offer enhanced durability and resistance to dents, which will reflect in a higher price per square foot. Higher-grade wood siding, with tighter knots and fewer imperfections, generally commands a higher price. Steel siding with heavier gauge and superior coatings can be more expensive, while fiber cement siding in thicker formulations or with higher-quality finishes might be more costly.
Vinyl Siding Cost Breakdown (per square foot)
| Vinyl Siding Feature | Approximate Cost (USD/sq ft) |
|---|---|
| Standard 10-mil vinyl siding, basic profile | $4 – $6 |
| Premium 10-mil vinyl siding, enhanced profile | $6 – $8 |
| 12-mil vinyl siding, enhanced durability | $7 – $9 |
| 12-mil vinyl siding, high-end profile with extended warranty | $9 – $12 |
Note: These are estimated figures. Actual costs can vary significantly depending on factors such as local labor costs, retailer markups, and specific siding brand and options.
Installation Costs and Labor
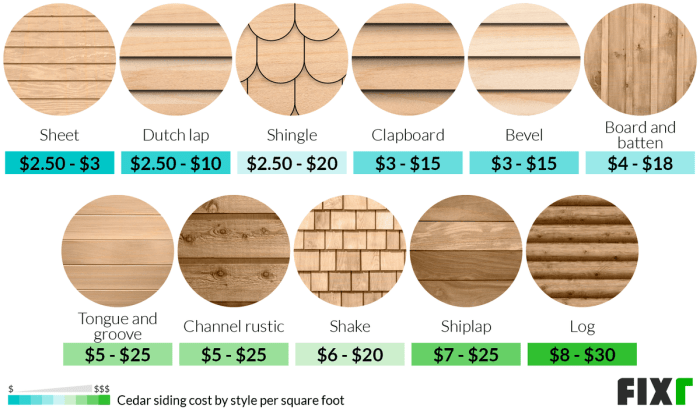
Source: fixr.com
Installation costs represent a significant portion of the overall siding project budget. Understanding the factors influencing these costs is crucial for homeowners to accurately estimate and manage their expenses. Factors like labor rates, contractor experience, project complexity, and chosen installation methods all contribute to the final price tag.
Labor costs for siding installation are influenced by a multitude of variables. Geographical location, local demand for skilled labor, and prevailing wage rates all play a role in determining the cost per hour or day. Moreover, the specific skills required for the chosen siding type and installation technique also affect the labor rate.
Factors Affecting Labor Costs
Labor costs for siding installation are directly correlated with the complexity of the project. A simple, straightforward installation on a standard-sized house will command a lower labor cost compared to a complex project involving challenging terrain, unusual siding types, or extensive repairs. Additionally, the time required to complete the project plays a significant role, as higher labor costs will typically apply to projects with longer completion times.
Contractor Experience and Reputation
Contractor experience and reputation significantly impact pricing. Established, reputable contractors often charge higher rates for their services, reflecting their proven track record, skilled workforce, and adherence to quality standards. This higher cost often translates to more reliable workmanship and a reduced risk of project delays or errors. Conversely, less experienced contractors may offer lower prices but may also carry a higher risk of subpar workmanship or project complications.
Project Complexity
The complexity of the siding project directly affects labor costs. Projects involving intricate designs, multiple siding types, or extensive repairs will require more labor hours and specialized expertise. A simple replacement of existing siding on a standard home will typically be less costly than a full-scale renovation project that requires extensive structural work, specialized materials, and extensive preparation. For instance, a project involving the installation of composite siding on a house with multiple layers of existing siding and challenging architectural features will be more expensive than a straightforward installation on a simpler structure.
Impact of Different Installation Methods
Different installation methods, such as using different types of fasteners, can influence labor costs. Using specialized fasteners or adhering to specific installation guidelines for particular siding types may require additional training and expertise, resulting in higher labor costs. The choice of fasteners directly impacts the speed and efficiency of the installation process. For instance, using specialized clips for a particular siding type may require additional time and cost, while standard nails may suffice for other siding types.
Comparison of Average Labor Costs per Square Foot
| Siding Installation Method | Average Labor Cost per Square Foot (USD) |
|---|---|
| Standard Wood Siding (nails) | $5 – $8 |
| Vinyl Siding (nails) | $6 – $9 |
| Composite Siding (screws/clips) | $7 – $12 |
| Metal Siding (specialized fasteners) | $8 – $15 |
Note: These figures are approximate averages and can vary significantly based on factors such as geographic location, contractor experience, and project complexity.
Estimating Siding Costs
Accurately estimating siding costs is crucial for homeowners planning a renovation project. It allows for realistic budgeting and helps avoid unpleasant surprises during the installation process. This section details the steps involved in estimating siding costs, from calculating the surface area to securing quotes and factoring in labor.
Calculating Siding Area
A precise calculation of the siding area is foundational to any cost estimate. Inaccurate measurements lead to significant errors in the final cost. Several methods can be used, depending on the complexity of the home’s exterior. For simple structures, a tape measure and basic geometry suffice. For more intricate designs, consider using specialized software or engaging a professional estimator.
- For rectangular or simple shapes, calculate the area by multiplying the length by the width of each section of siding.
- For complex shapes, divide the siding surface into simpler geometric shapes. Calculate the area of each shape and sum the results to determine the total area.
- In cases involving gables, eaves, or other protrusions, account for these features in the calculation. Measure the relevant dimensions and apply appropriate formulas for calculating the area of triangles or trapezoids.
- Use a measuring tape for precision. Double-check measurements to ensure accuracy.
Obtaining Material Quotes
Obtaining accurate material quotes is essential for creating a comprehensive budget. Compare quotes from multiple reputable suppliers to identify the most competitive pricing. Factors like the material type, quantity, and delivery options will impact the final cost.
- Request detailed quotes that articulate the materials included, their quantity, and the associated pricing.
- Inquire about any potential discounts or bulk pricing options.
- Verify the quality of the materials to ensure they meet your requirements and local building codes.
- Confirm that delivery schedules and installation procedures are included in the quote. This ensures you understand all aspects of the cost, including potential extra charges.
Estimating Labor Costs
Estimating labor costs requires considering several factors, such as the complexity of the project, the experience level of the installers, and local labor rates. Consult with siding contractors for accurate labor cost estimations based on the specific project scope.
- Consider the complexity of the project. Homes with intricate designs or significant surface areas will have higher labor costs.
- Inquire about the experience and qualifications of the installers. Experienced professionals typically command higher labor rates.
- Obtain quotes from several contractors to compare pricing and determine the most competitive rates.
- Ensure the labor quote includes all necessary tasks, such as material handling, installation, and cleanup.
Cost Breakdown Table
This table demonstrates how to break down the total cost per square foot of a siding project.
| Item | Cost per Square Foot (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| Siding Material | $5-15 |
| Installation Labor | $3-10 |
| Permitting and Inspection Fees | $0-50 |
| Total Cost per Square Foot | $8-30 |
Note: The estimated cost per square foot in the table is a broad range and can vary significantly based on specific factors such as material choice, labor rates, and local regulations.
DIY vs. Professional Installation
Choosing between DIY and professional siding installation involves weighing the financial implications, time commitment, and potential risks. The cost-effectiveness and complexity of the project are key factors in making this decision. A thorough understanding of both approaches is crucial for homeowners considering this significant home improvement.
Cost Comparison
A significant aspect of the decision process is the cost comparison between DIY and professional installation. While DIY can potentially save money, it also carries the risk of higher overall costs due to potential errors or the need for additional repairs. Professional installers, while more expensive upfront, often offer warranties and guarantee the quality of the work.
Advantages of DIY Installation
DIY siding installation presents certain advantages. Firstly, it can significantly reduce labor costs. Secondly, homeowners have greater control over the process and can customize the installation to their specific needs and preferences. Thirdly, it allows homeowners to gain valuable hands-on experience with home improvement projects.
Disadvantages of DIY Installation
DIY siding installation also has its drawbacks. Homeowners may lack the necessary skills and experience, potentially leading to errors in installation. Furthermore, procuring the right tools and materials can be time-consuming and costly. Finally, the project may take significantly longer than expected, impacting the overall timeline.
Potential Risks and Challenges of DIY Projects
DIY siding projects can present various risks and challenges. Improper installation can lead to water damage, structural issues, and costly repairs. Incorrect measurements and material selection can also negatively impact the outcome. The potential for injuries from handling heavy materials or using power tools is another important consideration.
Tools and Materials for DIY Installation
A range of tools and materials is necessary for a successful DIY siding installation. Essential tools include measuring tapes, power drills, saws, and level tools. Materials required may include the chosen siding type, nails, screws, and caulk. Detailed instructions and diagrams are essential for guidance during the installation process.
Example Tools and Materials
- Measuring tape, level, pencil, and utility knife
- Power drill, screwdriver, and saw
- Safety glasses, gloves, and work boots
- Siding panels, nails, screws, caulk, and sealant
- Ladder, scaffolding (if necessary), and appropriate protective gear
Average Costs Comparison
The following table provides a general comparison of average costs for DIY versus professional siding installation. It’s crucial to remember that these are estimates and actual costs can vary based on project specifics.
| Category | DIY | Professional |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $2,000 – $5,000 | $2,000 – $5,000 |
| Labor | $0 – $500 (depending on the level of help needed) | $3,000 – $10,000 (depending on size and complexity) |
| Total Cost | $2,000 – $5,500 | $5,000 – $15,000 |
Siding Cost Comparison Across Different Materials
Choosing the right siding material is crucial for both the initial cost and the long-term value of your home. Different siding types offer varying levels of durability, maintenance needs, and aesthetic appeal, which directly impact the overall cost of the project. Understanding the comparative costs and long-term implications of each material is essential for informed decision-making.
Vinyl Siding Costs
Vinyl siding is a popular choice due to its affordability and low maintenance. Its cost-effectiveness often makes it an attractive option for homeowners. The upfront cost per square foot is generally lower compared to other materials, though this can vary depending on the specific type of vinyl siding and the local market conditions. However, it’s essential to consider the potential long-term costs associated with repairs or replacements if the material is damaged or deteriorates.
Wood Siding Costs, Siding cost per square foot
Wood siding offers a classic, natural look, but it comes with higher upfront costs and more maintenance requirements. While the initial cost per square foot might be higher than vinyl, the aesthetic appeal and character it brings to a home often justify the price for some homeowners. Regular maintenance, including painting or staining, is crucial to preserve the beauty and longevity of wood siding. These maintenance tasks add to the overall long-term cost. The cost of repairs or replacements due to rot or insect damage can also be significant.
Fiber Cement Siding Costs
Fiber cement siding provides a balance between durability and aesthetic appeal, with a moderate cost per square foot. It combines the strength of cement with the aesthetic qualities of wood, offering a relatively low-maintenance option compared to wood. The cost per square foot is typically higher than vinyl but lower than many types of high-end wood siding. Fiber cement siding generally has a longer lifespan and requires less maintenance than wood, translating to lower long-term costs associated with repairs and replacements.
Maintenance Costs and Durability
The long-term cost of siding is heavily influenced by its durability and the frequency of required maintenance. Vinyl siding typically requires minimal maintenance, reducing the ongoing costs. Wood siding, while visually appealing, demands more upkeep, including painting or staining, increasing the long-term costs. Fiber cement siding strikes a balance, offering a good combination of durability and low maintenance. The lifespan of each material also plays a crucial role in long-term costs. Vinyl siding generally has a shorter lifespan compared to fiber cement.
Comparative Table of Siding Materials
| Siding Material | Approximate Cost per Square Foot (USD) | Maintenance Requirements | Durability & Lifespan | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $5-$15 | Low (minimal cleaning) | 15-25 years | Affordable, low maintenance, variety of colors and styles | Susceptible to damage from impact, less durable than other options |
| Wood | $10-$25 | High (painting/staining every few years, potential for rot or insect damage) | 25-40 years (with proper maintenance) | Aesthetically pleasing, natural look | High maintenance costs, susceptible to damage from weather and insects |
| Fiber Cement | $15-$30 | Moderate (occasional cleaning) | 50+ years | Durable, low-maintenance, resists rot and damage | Higher initial cost, limited color options compared to vinyl |
Tips for Saving on Siding Costs
Reducing siding costs without sacrificing quality is achievable through strategic planning and informed decision-making. This involves understanding various options, negotiating effectively, and implementing cost-saving strategies at every stage of the project. Careful consideration of materials, installation methods, and potential discounts can significantly impact the overall project budget.
Negotiation Strategies with Contractors and Suppliers
Effective negotiation with contractors and suppliers is crucial for minimizing siding costs. Understanding their pricing structures and being prepared with alternative options allows for more favorable agreements. This involves researching market rates, comparing quotes from multiple vendors, and presenting a clear budget. Presenting a firm but respectful negotiation stance, coupled with the ability to walk away if necessary, often yields better deals. Also, consider negotiating payment terms to gain leverage.
Cost-Effective Siding Materials
Selecting suitable, yet cost-effective siding materials is vital for reducing project costs. Options like vinyl siding, a popular and relatively inexpensive choice, are a good starting point. Its durability and low maintenance often offset the initial cost. Consider alternative wood siding types like cedar or pine, which offer a natural aesthetic, but may have higher maintenance requirements compared to vinyl. Comparing the long-term costs of maintenance, repair, and replacement, alongside initial costs, is important for a comprehensive analysis. A thorough evaluation of the available options, considering both short-term and long-term implications, is crucial for making an informed decision.
Installation Techniques for Cost Savings
Employing efficient and cost-effective installation techniques can contribute significantly to reducing overall costs. For instance, using pre-cut siding panels can speed up installation, reducing labor time and thus costs. Using pre-existing materials or components (like existing trim) where possible can also be a valuable strategy. Also, consider if DIY installation is feasible for certain tasks, which can save labor costs. Evaluating the balance between the time commitment and potential savings is essential for a successful DIY project.
Finding Discounted Siding Materials
Several resources can provide access to discounted siding materials. Checking online marketplaces, home improvement stores’ clearance sections, and local salvage yards are valuable avenues for finding discounted siding. Participating in local community forums and groups dedicated to home improvement may also reveal potential sources for reduced-cost materials. Additionally, contacting suppliers directly can sometimes lead to bulk discounts, especially if the project involves a large volume of materials.
Cost-Saving Tips for Different Project Stages
| Project Stage | Cost-Saving Tip |
|---|---|
| Material Selection | Compare prices from multiple suppliers, and look for discounted or clearance items. |
| Contractor Selection | Get multiple quotes from reputable contractors and compare their experience and qualifications. Check references and look for previous work samples. |
| Installation | Explore DIY installation options for tasks where skills and time allow. Pre-planning the installation process and organizing materials effectively can reduce labor time. |
| Project Management | Create a detailed project timeline and budget. Stick to the plan, and stay organized to minimize unexpected expenses. |
Final Review
In conclusion, calculating siding cost per square foot requires careful consideration of material type, regional variations, and installation specifics. Factors like material quality, labor costs, and installation methods all contribute to the final price. By understanding the interplay of these elements, homeowners can make well-informed decisions about their siding projects, ensuring a budget-friendly and aesthetically pleasing outcome. Remember, thorough research and careful planning are key to maximizing value and minimizing cost.





