Fiber Cement Siding vs Vinyl Siding A Comprehensive Comparison
Fiber cement siding vs vinyl siding: Choosing the right exterior cladding for your home is a significant decision. This comprehensive comparison delves into the key differences between these popular siding options, considering material properties, installation, aesthetics, cost, and environmental impact. Understanding the pros and cons of each will empower you to make an informed choice that aligns with your budget, lifestyle, and environmental values.
From the initial material composition to the long-term maintenance requirements, this analysis explores the intricacies of both fiber cement and vinyl siding. Factors such as durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal are critically examined. This detailed comparison will provide a clearer picture of which siding type best suits your specific needs and preferences.
Introduction
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding involves considering factors like cost, installation complexity, and long-term durability. Both materials offer attractive aesthetics and various color options, but their inherent properties and performance characteristics differ significantly. This comparison explores the historical context of siding materials, highlights key considerations, and presents a detailed comparison of fiber cement and vinyl siding. Understanding these factors allows homeowners to make informed decisions aligned with their specific needs and preferences.
Key Factors Influencing Siding Choice
Several factors play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate siding for a home. These include budgetary constraints, desired aesthetic appeal, the anticipated lifespan of the siding, and the ease and complexity of installation. The homeowner’s specific needs and preferences are paramount in the decision-making process.
Historical Context of Siding Materials
Siding materials have evolved considerably over time. Early homes often relied on materials like wood shingles or clapboard, which offered a natural aesthetic but were susceptible to weathering and required periodic maintenance. The development of synthetic materials like vinyl and fiber cement offered improved durability and reduced maintenance demands. This evolution reflects a continuous search for more efficient and long-lasting building materials.
Cost, Installation, and Longevity Comparison
This table summarizes the key differences in cost, installation, and longevity between fiber cement and vinyl siding. The presented data provides a comparative analysis of these important aspects for homeowners to make an informed decision.
| Feature | Fiber Cement Siding | Vinyl Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally higher upfront cost due to material and labor requirements. However, the long-term cost-effectiveness often outweighs initial investment. | Typically lower upfront cost, making it a more budget-friendly option for some homeowners. |
| Installation | Installation can be more complex, potentially requiring specialized tools and techniques. Installation time can be longer, and higher labor costs may apply. | Installation is generally easier and quicker, with fewer specialized tools and potentially lower labor costs. |
| Longevity | Known for exceptional durability and longevity, with a projected lifespan of 50 years or more under ideal conditions. | Vinyl siding offers a good lifespan, usually lasting 20-30 years with proper maintenance and installation. |
Material Properties and Performance
Fiber cement siding is composed of cement, cellulose fibers, and other additives. Its inherent strength and resistance to moisture and decay make it a robust choice for diverse climates. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, is a synthetic material that offers excellent resistance to dents, scratches, and fading.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of siding materials is a growing concern. While vinyl production can generate waste, the recyclability of vinyl offers an advantage. Fiber cement siding, due to its composition, has a lower carbon footprint compared to some other materials. Both options have their environmental pros and cons.
Material Properties
Fiber cement and vinyl siding are popular choices for exterior home cladding, each with unique characteristics affecting their performance and lifespan. Understanding their composition, manufacturing processes, and material properties is crucial for informed decision-making.
Fiber cement siding, a composite material, combines Portland cement, cellulose fibers, and other additives. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, is a rigid thermoplastic polymer, typically polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The differing compositions significantly impact their durability and long-term performance.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Fiber cement siding is manufactured by blending Portland cement with cellulose fibers, sand, and other additives. The mixture is then formed into panels, often through a process involving extruding or molding, and then cured. Vinyl siding production typically involves extruding molten PVC resin into various shapes and profiles. The resulting material is then cut, profiled, and often colored or textured.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Fiber cement siding demonstrates excellent durability, resisting rot, insect infestation, and moisture damage. Its inherent strength and resistance to weathering make it a robust choice for long-term exterior cladding. Vinyl siding is also remarkably durable. Its resistance to moisture and rot makes it a viable alternative to wood siding. However, both materials have limitations. Fiber cement is susceptible to cracking under extreme temperature fluctuations, while vinyl siding can be prone to damage from impact or prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Resistance to Pests
Both materials are generally resistant to common wood-destroying pests, such as termites and carpenter ants. Fiber cement’s inherent composition makes it a very effective deterrent to pests. Vinyl siding’s non-porous nature also makes it less attractive to these pests. However, proper installation and maintenance are crucial for both materials to prevent potential issues.
Market Options
A wide array of fiber cement and vinyl siding options are available in the market, ranging from standard colors and profiles to more specialized designs. Fiber cement siding is often available in a variety of colors and textures to match architectural styles. Vinyl siding also comes in diverse colors, styles, and profiles, often with options for enhanced durability or aesthetic appeal. Specific examples include James Hardie fiber cement siding, known for its durability and diverse color options, and various PVC vinyl siding brands with varied designs and finishes.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of fiber cement and vinyl siding is a complex issue. Fiber cement siding, due to its composition, can contain Portland cement, which has an associated carbon footprint. Vinyl siding production involves the use of PVC, a petrochemical-derived material. The manufacturing processes for both types of siding can generate waste, but recycling options exist for both. Care should be taken to ensure proper disposal and recycling of both materials to minimize environmental impact. The environmental footprint of both materials varies based on the specific manufacturing processes, energy sources used, and waste management practices.
Types of Siding
| Type of Siding | Composition | Durability | Weather Resistance | Pest Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Cement | Portland cement, cellulose fibers, and additives | High | Excellent | Excellent |
| Vinyl | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | High | Good | Good |
The table above summarizes the key characteristics of fiber cement and vinyl siding, highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses in terms of composition, durability, and resistance to pests. Choosing the appropriate siding material depends on factors such as budget, aesthetic preferences, and local environmental conditions.
Installation and Maintenance
Installing and maintaining siding is crucial for a home’s longevity and aesthetic appeal. Proper installation minimizes future issues, while consistent maintenance prolongs the siding’s lifespan and value. Understanding the nuances of each material is key to making informed decisions.
Installation Procedures
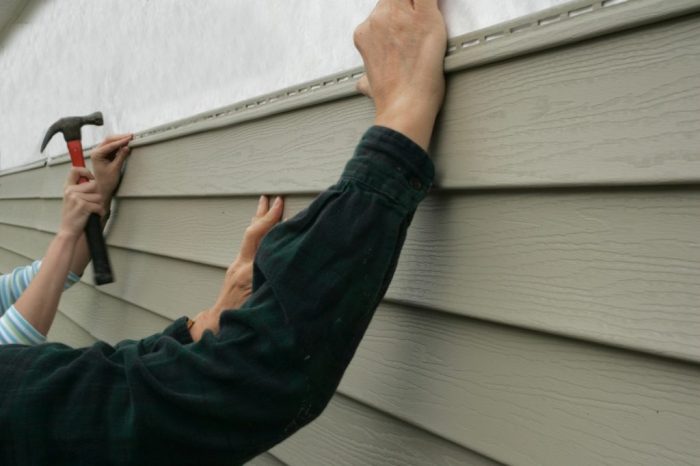
Fiber cement siding installation typically involves adhering panels to the existing sheathing using specialized adhesives and fasteners. This process often requires careful measuring, cutting, and precise placement to ensure a seamless finish. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, is often installed by nailing or clipping the panels to the framing, a process generally considered simpler and faster. However, both types of siding necessitate adherence to building codes and manufacturer specifications for optimal performance.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular cleaning and inspection are essential for both fiber cement and vinyl siding. Fiber cement siding, due to its durability, generally requires less frequent cleaning than vinyl. However, both materials benefit from periodic cleaning to remove dirt, debris, and mildew. For vinyl siding, cleaning with mild soap and water is often sufficient. For fiber cement, more aggressive cleaning methods might be needed, though these should be tested on a small, inconspicuous area first to avoid damage. Addressing minor repairs promptly, like patching holes or replacing damaged panels, is crucial for both materials.
DIY vs. Professional Installation
DIY installation of siding can be appealing for cost savings, but it carries risks. Incorrect installation can lead to leaks, drafts, and premature material failure. Professionals possess the expertise and tools to ensure proper installation, adhering to building codes and manufacturer recommendations. This often translates to a more robust and enduring structure. For complex projects or situations involving multiple layers, or where the home’s structure has significant flaws, professional installation is highly recommended.
Potential Installation Challenges and Solutions
A common challenge in fiber cement siding installation is achieving a seamless transition between panels. Solutions include using specialized corner pieces and carefully measuring the panels for proper alignment. Vinyl siding installation can be problematic when dealing with uneven surfaces. Solutions include using shims to level the panels and ensuring the underlayment is properly installed. Proper preparation of the wall surface, including adequate ventilation, is key for both types of siding.
Summary of Installation Steps
| Siding Type | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Cement | Measure and cut panels according to the structure. | Apply adhesive to the wall and panels. | Secure panels to the wall with appropriate fasteners. |
| Vinyl | Measure and cut panels according to the structure. | Ensure the surface is level. | Fasten panels to the wall using nails or clips. |
Aesthetics and Design
Fiber cement and vinyl siding offer a diverse range of aesthetic options, allowing homeowners to customize their homes’ appearance. Both materials are available in a multitude of colors, textures, and finishes, impacting curb appeal and the overall visual appeal of the property. This section explores the aesthetic possibilities of each material, focusing on their ability to mimic natural materials and the range of colors and finishes available.
The aesthetic choices homeowners make for their siding significantly influence the overall curb appeal of a home. A well-chosen siding material and finish can enhance the home’s visual appeal, while poor choices can detract from its attractiveness. The discussion will highlight the nuances of each material’s aesthetic capabilities, helping homeowners make informed decisions.
Aesthetic Options for Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding offers a wide array of aesthetic options, allowing homeowners to achieve a variety of styles. Its inherent strength and durability mean that it can withstand harsh weather conditions without compromising its aesthetic integrity.
- Mimicking Natural Materials: Fiber cement siding excels at replicating the look of natural materials like wood and stone. Manufacturers often create textures and finishes that closely resemble the appearance of wood planks or stone veneers, providing a visually appealing and authentic touch. Examples include siding that mimics the grain of cedar or the rough texture of slate. This ability to replicate natural materials adds to the home’s visual appeal and creates a sense of continuity with the surrounding landscape.
- Color and Finishes: A broad spectrum of colors and finishes are available for fiber cement siding, ranging from traditional neutrals to bold and vibrant hues. These options allow homeowners to match their desired aesthetic preferences. Finishes can range from smooth to textured, mimicking the natural variations of wood or stone.
Aesthetic Options for Vinyl Siding, Fiber cement siding vs vinyl siding
Vinyl siding is known for its affordability and ease of installation, but its aesthetic versatility has also evolved significantly.
- Mimicking Natural Materials: Vinyl siding can effectively mimic the appearance of wood, stone, and other natural materials. Advanced manufacturing processes allow for the creation of detailed textures and finishes that closely resemble the look of wood planks, stone, or even brick. This ability to emulate natural materials makes vinyl siding an attractive choice for homeowners seeking a natural aesthetic without the maintenance concerns associated with real wood or stone.
- Color and Finishes: A vast array of colors and finishes are available for vinyl siding, offering homeowners considerable flexibility in customizing their home’s exterior. From classic white and beige to bold and contemporary colors, vinyl siding can be tailored to match virtually any architectural style. Many vinyl siding options feature realistic wood grain patterns, adding a touch of natural charm.
Comparing Aesthetic Options
The following table summarizes the aesthetic options for fiber cement and vinyl siding, highlighting their respective strengths and limitations.
| Feature | Fiber Cement Siding | Vinyl Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Mimicking Natural Materials | Excellent; strong resemblance to wood and stone | Good; effective replication of natural materials |
| Color Options | Extensive range; from neutrals to vibrant colors | Extensive range; from neutrals to vibrant colors |
| Finishes | Smooth, textured, wood-grain, and stone-like | Smooth, textured, wood-grain, and stone-like |
| Curb Appeal Impact | High; durable and aesthetically pleasing | High; cost-effective and visually appealing |
Cost and Value: Fiber Cement Siding Vs Vinyl Siding

Source: angi.com
Comparing the upfront and long-term costs of fiber cement and vinyl siding is crucial for homeowners. Factors like material costs, labor expenses, and potential future maintenance play a significant role in the overall value proposition of each siding type. Understanding these aspects helps homeowners make informed decisions aligning with their budget and long-term needs.
Material Costs
Material costs for siding are influenced by factors such as material availability, market fluctuations, and regional demand. Fiber cement siding, often manufactured from a blend of cement, wood fiber, and other additives, can have a higher initial material cost than vinyl siding, which is primarily composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This difference in raw material composition and manufacturing processes affects the price.
Labor Costs
Labor costs for installation are another important factor. Installation complexity, labor availability, and local wage rates can influence the total labor costs. Fiber cement siding often requires more specialized installation techniques due to its rigidity and weight, potentially leading to higher labor costs compared to vinyl siding. However, the longevity of the installation may offset some of the higher initial labor costs over time.
Installation Costs
Installation costs vary based on the project size, the complexity of the installation, and the location. Larger projects, intricate designs, and challenging terrains can increase installation costs for both fiber cement and vinyl siding. For instance, a large, multi-story home with complex architectural features will likely have a higher installation cost for either siding type than a smaller, simpler home.
Cost Scenarios
Different project sizes and locations will result in varying cost scenarios. A small, simple home in a rural area might have a lower installation cost for both siding types compared to a larger, complex home in a densely populated urban area. Factors like the condition of the existing structure, the amount of preparation work needed, and the complexity of the project all contribute to the final cost. For example, replacing siding on a house with significant existing damage will likely cost more than a simple replacement on a well-maintained house.
Long-Term Value
Long-term value encompasses factors such as maintenance, repairs, and potential resale value. Fiber cement siding’s durability and resistance to rot, pests, and fire often translate to lower long-term maintenance costs. Vinyl siding, while relatively low-maintenance, might require more frequent repairs due to potential damage from impacts, weathering, or UV exposure. Resale value depends on the overall condition and desirability of the home.
Return on Investment (ROI)
The ROI of fiber cement and vinyl siding can be evaluated over time. Fiber cement’s longevity and low maintenance translate into a potentially higher ROI in the long run, offsetting the potentially higher upfront costs. However, the ROI of vinyl siding might be more attractive for homeowners prioritizing lower upfront costs and quicker returns, especially when considering lower maintenance requirements for a shorter time frame.
Cost Breakdown Table
| Siding Type | Material Cost (estimated) | Labor Cost (estimated) | Installation Cost (estimated) | Total Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Cement | $10-$15/sq ft | $5-$10/sq ft | $5-$10/sq ft | $20-$30/sq ft |
| Vinyl | $5-$8/sq ft | $3-$5/sq ft | $3-$5/sq ft | $11-$16/sq ft |
Note: These are estimated costs and can vary significantly based on specific project details.
Environmental Considerations
Choosing siding materials involves more than just aesthetics and cost; environmental impact is a crucial factor. Both fiber cement and vinyl siding have varying footprints throughout their lifecycles, from production to disposal. Understanding these differences can guide responsible choices.
Production Impacts
The manufacturing processes for fiber cement and vinyl siding have distinct environmental effects. Fiber cement production typically requires more energy and resources due to the need for raw materials like cement, sand, and cellulose. Conversely, vinyl production, while relying on petroleum-based polymers, often has optimized processes that reduce waste and energy consumption compared to some older cement manufacturing methods. Examining the entire supply chain, including sourcing raw materials and transportation, can highlight the environmental burden of each material.
Installation Impacts
Installation practices significantly influence the environmental impact of siding. Fiber cement siding often requires more labor-intensive installation, potentially leading to increased waste if not carefully managed. Proper waste disposal and recycling of construction debris are key to minimizing the environmental footprint during installation. Vinyl siding installation, generally, is less labor-intensive and requires fewer materials to install, potentially leading to lower waste generation during installation.
Disposal Impacts
The end-of-life stage of siding presents another environmental consideration. Fiber cement siding, due to its composition, can be recycled into various materials, including aggregate for construction purposes. Vinyl siding, although recyclable, has lower recycling rates in some regions compared to fiber cement. The availability of recycling facilities and community participation are key factors in determining the actual environmental impact of disposal.
Energy Efficiency
The energy efficiency of siding directly affects its overall environmental performance. Both fiber cement and vinyl siding can contribute to a home’s energy efficiency. Fiber cement siding can offer superior insulation properties due to its material structure. Vinyl siding, when properly installed, can also offer decent insulation and reduce energy loss through the walls. Consideration of R-values and thermal conductivity can provide a deeper understanding of energy efficiency benefits.
Environmentally Friendly Alternatives and Practices
There are ways to minimize the environmental impact of both siding types. Using recycled content in the production of fiber cement siding can significantly reduce its environmental footprint. For vinyl siding, minimizing water usage during installation and opting for locally sourced materials are examples of eco-friendly practices. Promoting responsible disposal methods and supporting recycling programs are also essential.
Recyclability
Fiber cement siding has a higher recyclability rate than vinyl siding. Fiber cement can be easily recycled into new products, reducing the demand for virgin materials and lowering the overall environmental impact. Vinyl siding, while recyclable, often has lower recycling rates in some areas. The accessibility and availability of recycling facilities directly affect the recyclability of both materials.
Summary Table
| Characteristic | Fiber Cement Siding | Vinyl Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Production | Higher energy consumption, resource intensive, but recycling opportunities exist. | Potentially lower energy consumption, but reliant on petroleum-based polymers. |
| Installation | Potentially higher waste generation if not managed properly. | Generally lower waste generation. |
| Disposal | High recyclability, can be repurposed into new products. | Recyclable but lower recycling rates in some areas. |
| Energy Efficiency | Good insulation properties, potentially reducing energy consumption. | Good insulation properties, potentially reducing energy consumption. |
Durability and Lifespan

Source: sfwconstruction.com
Fiber cement and vinyl siding, while both popular choices, differ significantly in their durability and lifespan. Understanding the factors impacting each material’s longevity is crucial for homeowners making informed decisions. This section delves into the typical lifespan of each material, highlighting the effects of various environmental factors and presenting real-world examples.
Fiber cement siding, known for its strength and resilience, typically outperforms vinyl in terms of overall lifespan. However, vinyl siding offers a more affordable entry point and comes with its own advantages in specific conditions. Both materials are susceptible to damage from extreme weather, but their resistance varies considerably.
Typical Lifespan Under Various Conditions
The lifespan of siding is greatly affected by environmental conditions. Exposure to sunlight, moisture, and pests can all accelerate deterioration. Different climates will affect the longevity of siding in different ways. Factors like the intensity of sunlight, the frequency and severity of storms, and the presence of insects or other pests directly impact the materials’ lifespan.
Factors Affecting Longevity
Several factors influence the lifespan of both fiber cement and vinyl siding. Exposure to prolonged sunlight can lead to fading and cracking in vinyl, while fiber cement is more resistant to these effects. Moisture, another key factor, can cause rotting and warping in poorly installed vinyl siding, whereas fiber cement, with its inherent water resistance, is less susceptible to this problem. Similarly, pest infestation can significantly shorten the lifespan of both materials, with wood-boring insects posing a particular threat to vinyl siding.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Numerous case studies demonstrate the varying performance of fiber cement and vinyl siding over time. In regions with high UV exposure, fiber cement siding has consistently shown superior resistance to fading and cracking compared to vinyl. Conversely, in areas with milder climates and lower moisture levels, vinyl siding often provides a cost-effective and durable solution for many homeowners.
Resilience to Extreme Weather Events
Both materials exhibit varying levels of resilience to extreme weather events. Fiber cement siding is generally more resistant to high winds and hailstorms than vinyl. However, improperly installed siding of either material can be susceptible to damage during these events. In areas prone to hurricanes or significant snowfalls, the performance of the siding will be affected by its installation and quality.
Comparison Table
| Factor | Fiber Cement | Vinyl |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Lifespan (Moderate Conditions) | 25-50 years | 20-30 years |
| Typical Lifespan (Harsh Conditions) | 20-40 years | 15-25 years |
| Resistance to UV Exposure | Excellent | Moderate |
| Resistance to Moisture | Excellent | Moderate (if properly installed) |
| Resistance to Pests | Excellent | Moderate |
| Resilience to High Winds | High | Moderate |
Conclusion

Source: optimole.com
In conclusion, the choice between fiber cement and vinyl siding depends heavily on individual priorities. Fiber cement boasts superior durability and aesthetic versatility, but comes with a higher upfront cost. Vinyl siding, conversely, is more budget-friendly and easier to install, but might not match the longevity of fiber cement. This comparison highlights the crucial factors to consider when making your final decision. Careful consideration of the cost, maintenance, and environmental impact will ultimately guide you to the ideal siding solution for your home.